Product Description
Pet Pump Induction Motor
Motor Description:
1.Our motors performance(data) are per customers` requirments.
2.Motor wires are cooper and some could be used aluminium wire to save cost
3.Motors could be used ball bearing and oil bear(Sleeve bearing) both.
4.Insulation Class B/F
withstand voltage:1800V/S/0.5mA
Rotation:CW (view from the shaft side)
Noise<50dB
Interturn Isulation:>2100V
Operation Temperature/Humidity Range:-40°C to +65°C, 0%~95%
5.Safe,reliable, low noise, high performance,characteristics hard, good and stable starting, long life, etc.
6.Typical Application: Exhaust fan, air purifier, micro-oven, fan, induction cooker, refrigerator, pump, heater, hood oven, blwer, air conditioner, Heater machines, dehumidifiers,pump
7.Motor Specification as below chart
| Model | Power(w) | Voltage(V) | Speed(RPM) | Current(A) | Torque(nm) | Efficient(%) | Weight(KG) |
| 6676 | 55 | 230 | 1062 | 0.241 | 0.15 | 30.6 | 1 |
| 6676 | 49 | 120 | 1060 | 0.439 | 0.18 | 39.50% | 1 |
Fine Watt motor focus on offering motor solutions to smart products for home appliance ,like BLDC,Capacitor motor,shaded pole motor,universal motor and mini generator. Our motors are widely used in kitchen,air conditional,Ice chest,washing machine,etc. Customers locate not only in China domestic ,also oversea from Asia to European and Amecica. Our engineer with 20 years experience in motor design and development,win a lot of motor inovation technology award,Our engineer also provide technical support to other big facotry.we believe we always can find the best solution for your product.
Company FAQ
(1) Q: What kind motors you can provide?
A:For now,we mainly provide Kitchen Hood Motor,DC Motor,Gear Motor,Fan Motor Refrigerator Motor,Hair Dryer Motor Blender Motor Mixer Motor,
BLDC Motor,Shade Pole Motor,Capacitor Motor, PMDC Motor,Synchronous Motor,etc
(2) Q: Is it possible to visit your factory
A: Sure. We always like to meet our customer face to face,this is better for understanding.But please kindly keep us posted a few days in advance so we can make good arrangement.
(3) Q: Can I get some samples
A: It depends. If only a few samples for personal use or replacement, I am afraid it will be difficult for us to provide, because all of our motors are custom made and no stock available if there is no further needs. If just sample testing before the official order and our MOQ, price and other terms are acceptable, we will provide samples.
(4) Q: Is there a MOQ for your motors?
A: Yes. The MOQ is between 1000~10,000pcs for different models after sample approval.
But it’s also okay for us to accept smaller lots like a few dozens, hundreds or thousands
For the initial 3 orders after sample approval.For samples, there is no MOQ requirement. But the less the better (like no more than 5pcs) on condition that the quantity is enough in case any changes needed after initial testing.
(5)Q: What advantage do you have?
A: For motors, we have quality guarantee, if there is probelm motor after inspection in customer house,we will replace .
For service, we offer 24 hours technical support and barrier-free communication with excellent service people.
Technical service: Except offer actual motor products,we can also offer motor technical supporting seperately to our customer.Our engineers are represent the most advanced techonogy.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal |
|---|---|
| Speed: | High Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

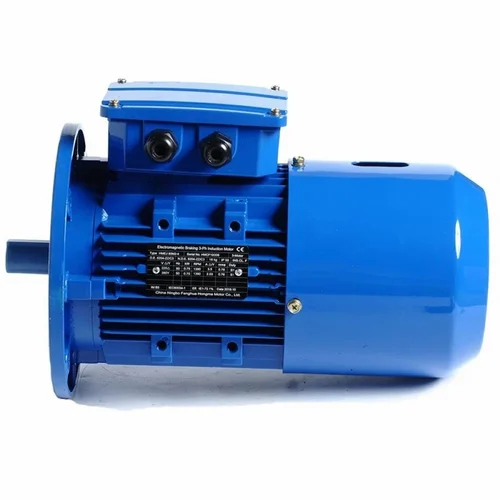
Can brake motors be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Brake motors can indeed be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments, provided they are appropriately designed and protected against the specific conditions they will encounter. The adaptability of brake motors allows them to function effectively and safely in diverse operating environments. Here’s a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor settings:
- Indoor Adaptation: Brake motors intended for indoor use are typically designed to meet the specific requirements of indoor environments. They are often constructed with enclosures that protect the motor from dust, debris, and moisture commonly found indoors. These enclosures can be in the form of drip-proof (DP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) designs. The enclosures prevent contaminants from entering the motor and ensure reliable and efficient operation in indoor settings.
- Outdoor Adaptation: When brake motors are required for outdoor applications, they need to be adapted to withstand the challenges posed by outdoor conditions, such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to elements. Outdoor-rated brake motors are designed with additional protective measures to ensure their durability and performance. They may feature weatherproof enclosures, such as totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) enclosures with added gaskets and seals to prevent water ingress. These enclosures provide effective protection against rain, snow, dust, and other outdoor elements, allowing the motor to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
- Environmental Sealing: Brake motors can be equipped with environmental seals to further enhance their adaptability for both indoor and outdoor use. These seals provide an additional layer of protection against the entry of moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Depending on the specific application requirements, the seals can be applied to the motor’s shaft, housing, or other vulnerable areas to ensure proper sealing and prevent damage or performance degradation due to environmental factors.
- Corrosion Resistance: In certain outdoor environments or specific indoor settings with corrosive elements, brake motors can be designed with corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These specialized materials, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, provide protection against corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt air. Corrosion-resistant brake motors are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance in corrosive environments.
- Temperature Considerations: Brake motors must be adapted to handle the temperature ranges encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. For indoor applications, motors may be designed to operate within a specific temperature range, ensuring reliable performance without overheating. Outdoor-rated brake motors may have additional cooling features, such as oversized cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat effectively and operate within acceptable temperature limits. Heating elements can also be incorporated to prevent condensation and maintain optimal operating temperatures in outdoor or highly humid indoor environments.
- IP Rating: In addition to the specific adaptations mentioned above, brake motors for both indoor and outdoor use are often assigned an Ingress Protection (IP) rating. The IP rating indicates the motor’s level of protection against solid particles (first digit) and water ingress (second digit). The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection offered. IP ratings help users select brake motors that are suitable for their intended environment by considering factors such as dust resistance, water resistance, and overall environmental durability.
By incorporating appropriate enclosures, environmental seals, corrosion-resistant materials, temperature management features, and IP ratings, brake motors can be successfully adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments. These adaptations ensure that the motors are well-protected, perform reliably, and maintain their efficiency and longevity, regardless of the operating conditions they are exposed to.

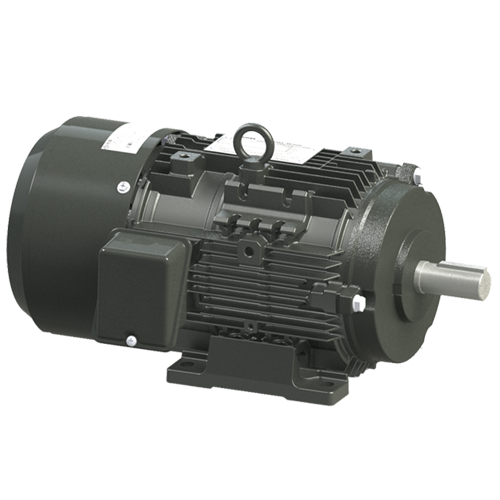
How do brake motors contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling?
Brake motors play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. They provide several advantages that improve the overall performance and productivity of these systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how brake motors contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling:
- Precise Control: Brake motors offer precise control over the movement of conveyor systems. The braking mechanism allows for quick and accurate stopping, starting, and positioning of the conveyor belt or other material handling components. This precise control ensures efficient operation, minimizing the time and effort required to handle materials and reducing the risk of damage or accidents.
- Speed Regulation: Brake motors can regulate the speed of conveyor systems, allowing operators to adjust the conveying speed according to the specific requirements of the materials being handled. This speed control capability enables efficient material flow, optimizing production processes and preventing bottlenecks or congestion. It also contributes to better synchronization with upstream or downstream processes, improving overall system efficiency.
- Load Handling: Brake motors are designed to handle varying loads encountered in material handling applications. They provide the necessary power and torque to move heavy loads along the conveyor system smoothly and efficiently. The braking mechanism ensures safe and controlled stopping even with substantial loads, preventing excessive wear or damage to the system and facilitating efficient material transfer.
- Energy Efficiency: Brake motors are engineered for energy efficiency, contributing to cost savings and sustainability in material handling operations. They are designed to minimize energy consumption during operation by optimizing motor efficiency, reducing heat losses, and utilizing regenerative braking techniques. Energy-efficient brake motors help lower electricity consumption, resulting in reduced operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Safety Enhancements: Brake motors incorporate safety features that enhance the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling by safeguarding personnel and equipment. They are equipped with braking systems that provide reliable stopping power, preventing unintended motion or runaway loads. Emergency stop functionality adds an extra layer of safety, allowing immediate halting of the system in case of emergencies or hazards, thereby minimizing the potential for accidents and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Reliability and Durability: Brake motors are constructed to withstand the demanding conditions of material handling environments. They are designed with robust components and built-in protection features to ensure reliable operation even in harsh or challenging conditions. The durability of brake motors reduces downtime due to motor failures or maintenance issues, resulting in improved system efficiency and increased productivity.
- Integration and Automation: Brake motors can be seamlessly integrated into automated material handling systems, enabling efficient and streamlined operations. They can be synchronized with control systems and sensors to optimize material flow, automate processes, and enable efficient sorting, routing, or accumulation of items. This integration and automation capability enhances system efficiency, reduces manual intervention, and enables real-time monitoring and control of the material handling process.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Brake motors are designed for ease of maintenance and serviceability, which contributes to the overall efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. They often feature modular designs that allow quick and easy replacement of components, minimizing downtime during maintenance or repairs. Accessible lubrication points, inspection ports, and diagnostic features simplify routine maintenance tasks, ensuring that the motors remain in optimal working condition and maximizing system uptime.
By providing precise control, speed regulation, reliable load handling, energy efficiency, safety enhancements, durability, integration with automation systems, and ease of maintenance, brake motors significantly contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. Their performance and features optimize material flow, reduce downtime, enhance safety, lower operating costs, and improve overall productivity in a wide range of industries and applications.

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-04-29
China best Induction Motor Asynchronous Electric Electromagnetic Brake Three Phase Scooters Generators Controller Linear High Speed Drive Exoesqueleto Elevator Gear Motor with Best Sales
Product Description
Induction Motor Asynchronous Electric Electromagnetic Brake Three Phase Scooters Generators Controller Linear High Speed Drive Exoesqueleto Elevator Gear Motor
Application of Induction Motor
Induction motors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Pumps: Induction motors are used in pumps to move fluids, such as water, oil, and chemicals.
- Fans: Induction motors are used in fans to circulate air, such as in homes, offices, and factories.
- Compressors: Induction motors are used in compressors to compress gases, such as air and refrigerants.
- Conveyors: Induction motors are used in conveyors to move materials, such as food, parts, and packages.
- Machine tools: Induction motors are used in machine tools to power a variety of tools, such as drills, saws, and lathes.
- Elevators: Induction motors are used in elevators to power the hoisting mechanism.
- Wind turbines: Induction motors are used in wind turbines to convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy.
- Other: Induction motors are also used in a variety of other applications, such as washing machines, dryers, and air conditioners.
Induction motors are a type of electric motor that uses a rotating magnetic field to induce current in the rotor, which causes the rotor to turn. Induction motors are typically used in applications where a constant speed is required, such as in pumps, fans, and conveyors. Induction motors are also used in applications where a high starting torque is required, such as in elevators and wind turbines.
Induction motors are a reliable and efficient type of electric motor. They are relatively inexpensive to purchase and maintain. Induction motors are also easy to install and operate.
Here are some of the advantages of using induction motors:
- Reliable: Induction motors are very reliable and have a long lifespan.
- Efficient: Induction motors are very efficient, converting up to 90% of the input power into output power.
- Inexpensive: Induction motors are relatively inexpensive to purchase and maintain.
- Easy to install and operate: Induction motors are easy to install and operate.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using induction motors:
- Low starting torque: Induction motors have a low starting torque, which means that they may not be suitable for applications where a high starting torque is required.
- Noise: Induction motors can be noisy, especially at high speeds.
- Vibration: Induction motors can vibrate, especially at high speeds.
Overall, induction motors are a reliable and efficient type of electric motor that is used in a wide variety of applications. They are relatively inexpensive to purchase and maintain, and they are easy to install and operate.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | – |
| Number of Stator: | – |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | – |
| Number of Poles: | – |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
Can brake motors be used in conjunction with other motion control methods?
Yes, brake motors can be used in conjunction with other motion control methods to achieve precise and efficient control over mechanical systems. Brake motors provide braking functionality, while other motion control methods offer various means of controlling the speed, position, and acceleration of the system. Combining brake motors with other motion control methods allows for enhanced overall system performance and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be used in conjunction with other motion control methods:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Brake motors can be used in conjunction with VFDs, which are electronic devices that control the speed and torque of an electric motor. VFDs enable precise speed control, acceleration, and deceleration of the motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. By incorporating a brake motor with a VFD, the system benefits from both the braking capability of the motor and the advanced speed control provided by the VFD.
- Servo Systems: Servo systems are motion control systems that utilize servo motors and feedback mechanisms to achieve highly accurate control over position, velocity, and torque. In certain applications where rapid and precise positioning is required, brake motors can be used in conjunction with servo systems. The brake motor provides the braking function when the system needs to hold position or decelerate rapidly, while the servo system controls the dynamic motion and positioning tasks.
- Stepper Motor Control: Stepper motors are widely used in applications that require precise control over position and speed. Brake motors can be utilized alongside stepper motor control systems to provide braking functionality when the motor needs to hold position or prevent undesired movement. This combination allows for improved stability and control over the stepper motor system, especially in applications where holding torque and quick deceleration are important.
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Systems: In some industrial applications, hydraulic or pneumatic systems are used for motion control. Brake motors can be integrated into these systems to provide additional braking capability when needed. For example, a brake motor can be employed to hold a specific position or provide emergency braking in a hydraulic or pneumatic actuator system, enhancing safety and control.
- Control Algorithms and Systems: Brake motors can also be utilized in conjunction with various control algorithms and systems to achieve specific motion control objectives. These control algorithms can include closed-loop feedback control, PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control, or advanced motion control algorithms. By incorporating a brake motor into the system, the control algorithms can utilize the braking functionality to enhance overall system performance and stability.
The combination of brake motors with other motion control methods offers a wide range of possibilities for achieving precise, efficient, and safe control over mechanical systems. Whether it is in conjunction with VFDs, servo systems, stepper motor control, hydraulic or pneumatic systems, or specific control algorithms, brake motors can complement and enhance the functionality of other motion control methods. This integration allows for customized and optimized control solutions to meet the specific requirements of diverse applications.

Can you provide examples of machinery or equipment that frequently use brake motors?
In various industrial and manufacturing applications, brake motors are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment. These motors provide braking functionality and enhance the safety and control of rotating machinery. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that frequently utilize brake motors:
- Conveyor Systems: Brake motors are extensively used in conveyor systems, where they control the movement and stopping of conveyor belts. They ensure smooth and controlled starting, stopping, and positioning of material handling conveyors in industries such as logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing.
- Hoists and Cranes: Brake motors are employed in hoists and cranes to provide reliable load holding and controlled lifting operations. They ensure secure stopping and prevent unintended movement of loads during lifting, lowering, or suspension of heavy objects in construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and other settings.
- Elevators and Lifts: Brake motors are an integral part of elevator and lift systems. They facilitate controlled starting, stopping, and leveling of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and other structures.
- Metalworking Machinery: Brake motors are commonly used in metalworking machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. They enable precise control and stopping of rotating spindles, ensuring safe machining operations and preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled rotation.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Brake motors are found in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. They provide controlled stopping and precise positioning of printing cylinders, rollers, or packaging components, ensuring accurate printing, packaging, and labeling processes.
- Textile Machinery: In textile manufacturing, brake motors are used in various machinery, including spinning machines, looms, and winding machines. They enable controlled stopping and tension control of yarns, threads, or fabrics, enhancing safety and quality in textile production.
- Machine Tools: Brake motors are widely employed in machine tools such as grinders, saws, and machining centers. They enable controlled stopping and tool positioning, ensuring precise machining operations and minimizing the risk of tool breakage or workpiece damage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Brake motors are utilized in material handling equipment such as forklifts, pallet trucks, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). They provide controlled stopping and holding capabilities, enhancing the safety and stability of load transport and movement within warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
- Winches and Winders: Brake motors are commonly used in winches and winders for applications such as cable pulling, wire winding, or spooling operations. They ensure controlled stopping, load holding, and precise tension control, contributing to safe and efficient winching or winding processes.
- Industrial Fans and Blowers: Brake motors are employed in industrial fans and blowers used for ventilation, cooling, or air circulation purposes. They provide controlled stopping and prevent the fan or blower from freewheeling when power is turned off, ensuring safe operation and avoiding potential hazards.
These examples represent just a selection of the machinery and equipment where brake motors are frequently utilized. Brake motors are versatile components that enhance safety, control, and performance in numerous industrial applications, ensuring reliable stopping, load holding, and motion control in rotating machinery.

What is a brake motor and how does it operate?
A brake motor is a type of electric motor that incorporates a mechanical braking system. It is designed to provide both motor power and braking functionality in a single unit. The brake motor is commonly used in applications where rapid and precise stopping or holding of loads is required. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a brake motor is and how it operates:
A brake motor consists of two main components: the electric motor itself and a braking mechanism. The electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive a load. The braking mechanism, usually located at the non-drive end of the motor, provides the necessary braking force to stop or hold the load when the motor is turned off or power is cut off.
The braking mechanism in a brake motor typically employs one of the following types of brakes:
- Electromagnetic Brake: An electromagnetic brake is the most common type used in brake motors. It consists of an electromagnetic coil and a brake shoe or armature. When the motor is powered, the electromagnetic coil is energized, creating a magnetic field that attracts the brake shoe or armature. This releases the brake and allows the motor to rotate and drive the load. When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the electromagnetic coil is de-energized, and the brake shoe or armature is pressed against a stationary surface, creating friction and stopping the motor’s rotation.
- Mechanical Brake: Some brake motors use mechanical brakes, such as disc brakes or drum brakes. These brakes employ friction surfaces, such as brake pads or brake shoes, which are pressed against a rotating disc or drum attached to the motor shaft. When the motor is powered, the brake is disengaged, allowing the motor to rotate. When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, a mechanical mechanism, such as a spring or a cam, engages the brake, creating friction and stopping the motor’s rotation.
The operation of a brake motor involves the following steps:
- Motor Operation: When power is supplied to the brake motor, the electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is used to drive the load. The brake is disengaged, allowing the motor shaft to rotate freely.
- Stopping or Holding: When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism is engaged. In the case of an electromagnetic brake, the electromagnetic coil is de-energized, and the brake shoe or armature is pressed against a stationary surface, creating friction and stopping the motor’s rotation. In the case of a mechanical brake, a mechanical mechanism engages the brake pads or shoes against a rotating disc or drum, creating friction and stopping the motor’s rotation.
- Release and Restart: To restart the motor, power is supplied again, and the braking mechanism is disengaged. In the case of an electromagnetic brake, the electromagnetic coil is energized, releasing the brake shoe or armature. In the case of a mechanical brake, the mechanical mechanism disengages the brake pads or shoes from the rotating disc or drum.
Brake motors are commonly used in applications that require precise stopping or holding of loads, such as cranes, hoists, conveyors, machine tools, and elevators. The incorporation of a braking system within the motor eliminates the need for external braking devices or additional components, simplifying the design and installation process. Brake motors enhance safety, efficiency, and control in industrial applications by providing reliable and rapid braking capabilities.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China 15W AC 110V 220V single phase or three phase induction gear motor motor brushes
Model Number: 3IK15GN-C
Type: Induction Motor
Frequency: 50/60HZ
Phase: Single-phase
Efficiency: IE 1
Voltage: Single-phase AC110V,220V Three-phase AC220/380V
Certification: CCC, ce
Packaging Details: 15W AC 110V 220V single phase or 3 phase induction gear motor Motor Packing:Carton packaging
Port: XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.HN
Performance description:
1.The rotating mode is continuous.
2.E class insulation adopted
3.Stable performance with low noise
4.Balaneed wire winding is used and theerefore very convenient for reversible rotating Note : It’s just the typical technical data for you reference, We can produce motor according to customer’s requirement.
How to Assemble a Planetary Motor
A Planetary Motor uses multiple planetary surfaces to produce torque and rotational speed. The planetary system allows for a wide range of gear reductions. Planetary systems are particularly effective in applications where higher torques and torque density are needed. As such, they are a popular choice for electric vehicles and other applications where high-speed mobility is required. Nevertheless, there are many benefits associated with using a planetary motor. Read on to learn more about these motors.
VPLite
If you’re looking to replace the original VP, the VPLite has a similar output shaft as the original. This means that you can mix and match your original gear sets, including the input and output shafts. You can even mix metal inputs with plastic outputs. Moreover, if you decide to replace the gearbox, you can easily disassemble the entire unit and replace it with a new one without losing any output torque.
Compared to a planetary motor, a spur gear motor uses fewer gears and is therefore cheaper to produce. However, the latter isn’t suitable for high-torque applications. The torque produced by a planetary gearmotor is evenly distributed, which makes it ideal for applications that require higher torque. However, you may have to compromise on the torque output if you’re looking for a lightweight option.
The VersaPlanetary Lite gearbox replaces the aluminum ring gear with a 30% glass-filled nylon gear. This gearbox is available in two sizes, which means you can mix and match parts to get a better gear ratio. The VPLite gearbox also has a female 5mm hex output shaft. You can mix and match different gearboxes and planetary gearboxes for maximum efficiency.
VersaPlanetary
The VersaPlanetary is a highly versatile planetary motor that can be mounted in a variety of ways. Its unique design includes a removable shaft coupler system that makes it simple to swap out the motor with another. This planetary motor mounts in any position where a CIM motor mounts. Here’s how to assemble the motor. First, remove the hex output shaft from the VersaPlanetary output stage. Its single ring clip holds it in place. You can use a drill press to drill a hole into the output shaft.
After mounting the gearbox, you can then mount the motor. The mounting hardware included with the VersaPlanetary Planetary Motor comes with four 10-32 threaded holes on a two-inch bolt circle. You can use these holes to mount your VersaPlanetary on a CIM motor or a CIM-compatible motor. Once assembled, the VersaPlanetary gearbox has 72 different gear ratios.
The VersaPlanetary gearbox is interchangeable with regular planetary gearboxes. However, it does require additional parts. You can purchase a gearbox without the motor but you’ll need a pinion. The pinion attaches to the shaft of the motor. The gearbox is very sturdy and durable, so you won’t have to worry about it breaking or wearing out.
Self-centering planetary gears
A planetary motor is a simple mechanical device that rotates around a axis, with the planets moving around the shaft in a radial direction. The planets are positioned so that they mesh with both the sun gear and the output gears. The carrier 48 is flexibly connected to the drive shaft and can move depending on the forces exerted by the planet gears. In this way, the planets can always be in the optimal mesh with the output gears and sun gear.
The first step in developing a planetary gear motor is to identify the number of teeth in each planet. The number of teeth should be an integer. The tooth diameters of the planets should mesh with each other and the ring. Typically, the teeth of one planet must mesh with each other, but the spacing between them must be equal or greater than the other. This can be achieved by considering the tooth count of each planet, as well as the spacing between planets.
A second step is to align the planet gears with the output gears. In a planetary motor, self-centering planetary gears must be aligned with both input and output gears to provide maximum torque. For this to be possible, the planet gears must be connected with the output shaft and the input shaft. Similarly, the output shaft should also be able to align with the input gear.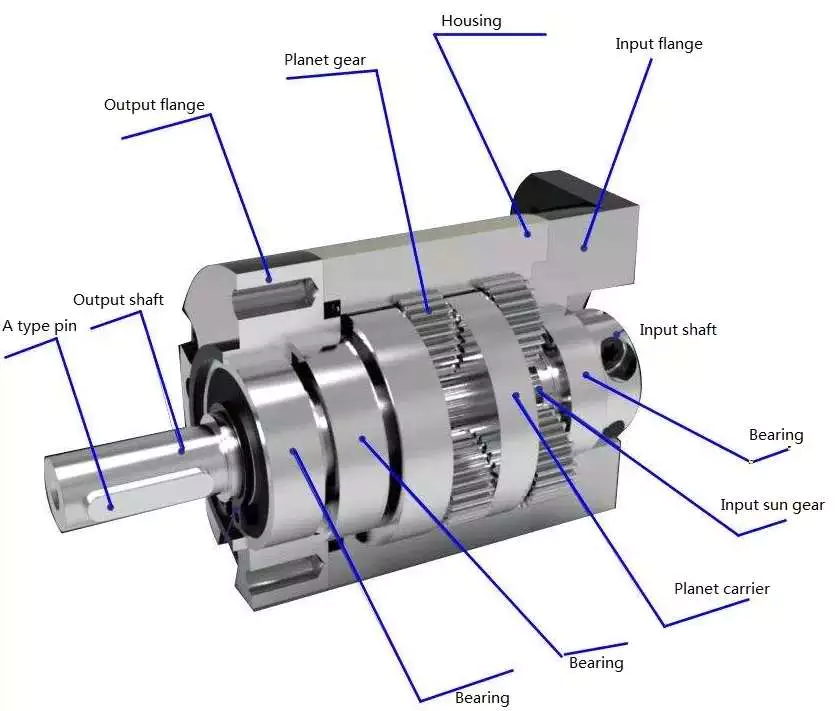
Encoders
A planetary geared motor is a DC motor with a planetary gearbox. The motor can be used to drive heavy loads and has a ratio of 104:1. The shaft speed is 116rpm when it is unloaded. A planetary gearbox has a low backlash and is often used in applications that need high torque. Planetary Motor encoders can help you keep track of your robot’s position or speed.
They are also able to control motor position and speed with precision. Most of them feature high resolution. A 0.18-degree resolution encoder will give you a minimum of 2000 transitions per rotation between outputs A and B. The encoder is built to industrial standards and has a sturdy gearbox to avoid damage. The encoder’s robust design means it will not stall when the motor reaches its maximum speed.
There are many advantages to a planetary motor encoder. A high-quality one will not lose its position or speed even if it’s subject to shocks. A good quality planetary motor will also last a long time. Planetary motors are great for resale or for your own project. If you’re considering buying a planetary motor, consider this information. It’ll help you decide if a particular model is right for your needs.
Cost
There are several advantages of planetary motors. One of the biggest is their cost, but they can also be used in many different applications. They can be combined with a variety of gearboxes, and are ideal for various types of robots, laboratory automation, and production applications. Planetary gearboxes are available in many different materials, and plastic planetary gearboxes are an economical alternative. Plastic gearboxes reduce noise at higher speeds, and steel input stage gears are available for high torques. A modified lubrication system can help with difficult operating conditions.
In addition to being more durable, planetary motors are much more efficient. They use fewer gears, which lowers the overall cost of production. Depending on the application, a planetary motor can be used to move a heavy object, but is generally less expensive than its counterpart. It is a better choice for situations where the load is relatively low and the motor is not used frequently. If you need a very high torque output, a planetary motor may be the better option.
Planetary gear units are a good choice for applications requiring high precision, high dynamics, and high torque density. They can be designed and built using TwinCAT and TC Motion Designer, and are delivered as complete motor and gear unit assemblies. In a few simple steps, you can calculate the torque required and compare the costs of different planetary gear units. You can then choose the best model for your application. And because planetary gear units are so efficient, they are a great option for high-end industrial applications.
Applications
There are several different applications of the planetary motor. One such application is in motion control. Planetary gearboxes have many benefits, including high torque, low backlash, and torsional stiffness. They also have an extremely compact design, and can be used for a variety of applications, from rack and pinion drives to delta robotics. In many cases, they are less expensive to manufacture and use than other types of motors.
Another application for planetary gear units is in rotary tables. These machines require high precision and low backlash for their precise positioning. Planetary gears are also necessary for noise reduction, which is a common feature in rotary tables. High precision planetary gears can make the height adjustment of OP tables a breeze. And because they are extremely durable and require low noise, they are a great choice for this application. In this case, the planetary gear is matched with an AM8000 series servomotor, which gives a wide range of choices.
The planetary gear transmission is also widely used in helicopters, automobiles, and marine applications. It is more advanced than a countershaft drive, and is capable of higher torque to weight ratios. Other advantages include its compact design and reduced noise. A key concern in the development of this type of transmission is to minimize vibration. If the output of a planetary gear transmission system is loud, the vibration caused by this type of drive system may be too loud for comfort.


editor by czh