Product Description
Product Description
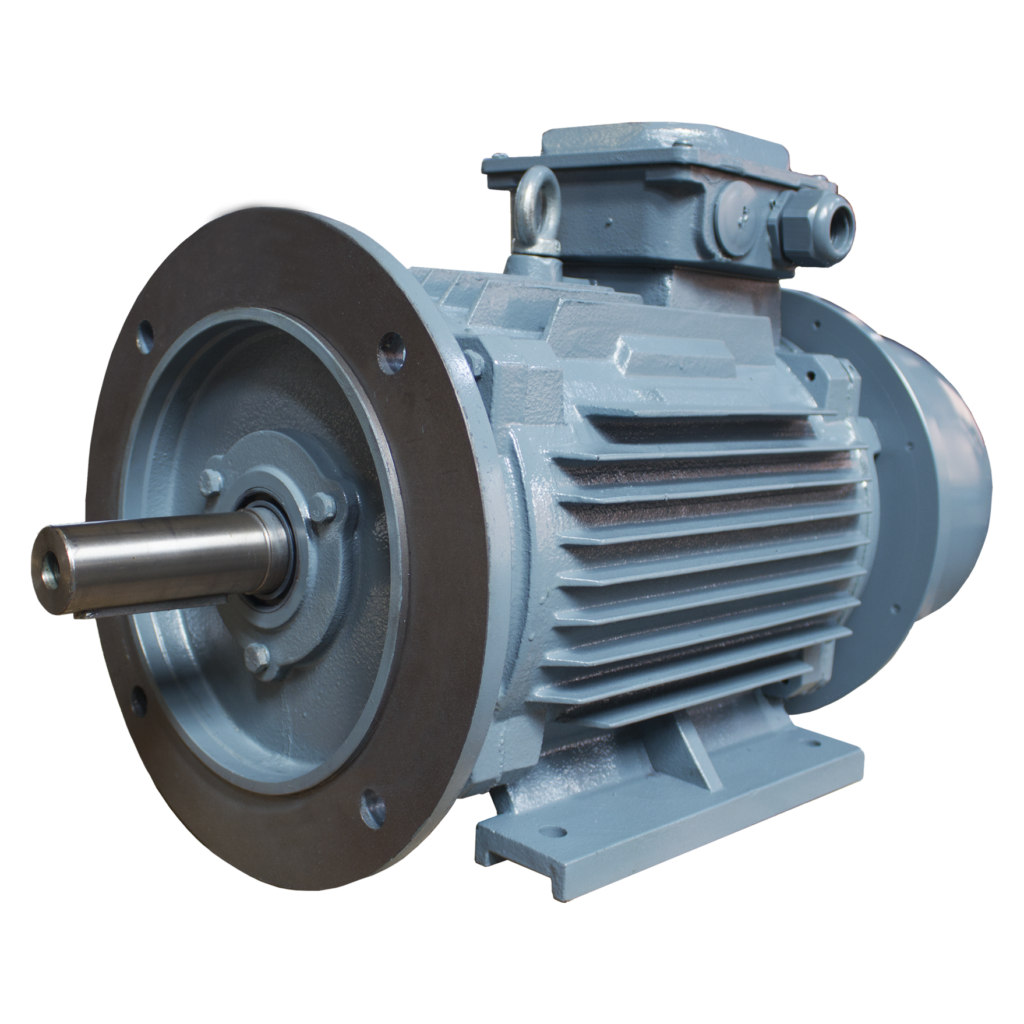
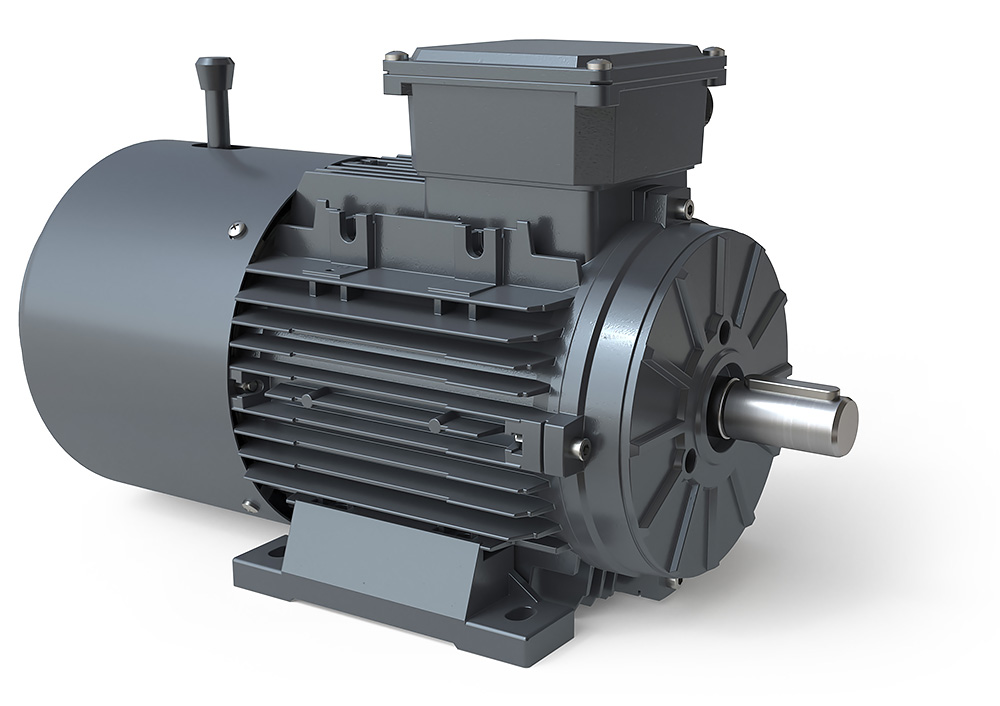
Yej Series Three Phase AC Induction Electromagnetic Brake Motor
YEJ2, YDEJ2 series electromagnetic brake motors are improved products of YEJ series. it is in accordance with JB/T6456
requirements, and its electrical performance is in accord with Y2 series technical standard.The electric power of the controller should be synchronized with the electric power of the motor.The electric motors are equipped the electromagnetic brake on the non-shaft end. when electricity off retarding disc will automatically press in end-shield which produce friction brake torque and stop the running of motor! the no-load brake duration is changed with the frame size of the motor the range is o.15-0.45 seconds. This kind of motor is considered as the driving force of
various machinery and widely used in mechanical workout machine tool, transport machinery,package, woodworking, food, chemical engineering, textile, construction,shop, roll door machinery
|
Model |
YEJ2-112M-4 |
|
Power |
4kw |
|
Speed |
1410r/min |
|
Current |
8.8A |
|
Efficiency |
84% |
|
Power factor |
0.82 |
|
Static Braking torque |
40N.m |
|
Mounting |
B3/B5/B35/B34 |
If you want more information, please consult me
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
Our Advantages
Company Profile
Certifications
FAQ
Q: Do you offer OEM service?
A: Yes, we can customize it as your request.
Q: What is your payment term?
A: TT. LC, AND WESTER UNION
Q: What is your lead time?
A: About 30 days after receiving deposit.
Q: What certificates do you have?
A: We have CE, ISO. And we can apply for specific certificate for different country such as SONCAP for Nigeria, SASO for Saudi Arabia, etc
Q: What about the warranty?
A: We offer 12month warranty period as the quality guarantee.
Q:What service do you offer?
A: Pre-sales service, in-sales service, after-sales service. If you become our local distributor, we can introduce end-customers to purchase from you.
Q:What’s your motor winding?
A: 100% copper winding
Q:Which port is near to you?
A: HangZhou port. And we can arrange to deliver HangZhou, ZheJiang , Urumqi, or other Chinese cities, too.
Q:Could you offer CHINAMFG Certification.
A: we can do as your request.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | High Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4pole |
| Samples: |
US$ 500/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment?
Brake motors play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and controlled movement in equipment by providing reliable braking functionality. They work in coordination with the motor and other control systems to achieve precise control over the motion of the equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment:
- Braking Capability: Brake motors are specifically designed to provide effective braking capability. When the power to the motor is cut off or when a braking signal is applied, the brake system engages, generating frictional forces that slow down and bring the equipment to a controlled stop. The brake torque generated by the motor helps prevent coasting or unintended movement, ensuring smooth and controlled deceleration.
- Quick Response Time: Brake motors are engineered to have a quick response time, meaning that the brake engages rapidly once the control signal is applied. This quick response time allows for prompt and precise control over the movement of the equipment. By minimizing the delay between the initiation of the braking action and the actual engagement of the brake, brake motors contribute to smooth and controlled movement.
- Adjustable Brake Torque: Brake motors often offer the ability to adjust the brake torque to suit the specific requirements of the equipment and application. The brake torque can be tailored to the load characteristics and operating conditions to achieve optimal braking performance. By adjusting the brake torque, brake motors ensure that the equipment decelerates smoothly and consistently, avoiding abrupt stops or jerky movements.
- Brake Release Mechanisms: In addition to providing braking action, brake motors incorporate mechanisms to release the brake when the equipment needs to resume motion. These release mechanisms can be controlled manually or automatically, depending on the application. The controlled release of the brake ensures that the equipment starts moving smoothly and gradually, allowing for controlled acceleration.
- Integration with Control Systems: Brake motors are integrated into the overall control systems of the equipment to achieve coordinated and synchronized movement. They work in conjunction with motor control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or servo systems, to precisely control the speed, acceleration, and deceleration of the equipment. By seamlessly integrating with the control systems, brake motors contribute to the smooth and controlled movement of the equipment.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Brake motors are designed and manufactured in compliance with safety standards and regulations. They undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure reliable and consistent braking performance. By adhering to safety standards, brake motors help prevent sudden or uncontrolled movements that could pose a safety risk and ensure the equipment operates within acceptable limits.
By providing effective braking capability, quick response time, adjustable brake torque, release mechanisms, integration with control systems, and compliance with safety standards, brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment. They enable precise control over the deceleration, stopping, and starting of the equipment, enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and overall performance.
What factors should be considered when selecting the right brake motor for a task?
When selecting the right brake motor for a task, several factors should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the specific application requirements. These factors help determine the suitability of the brake motor for the intended task and play a crucial role in achieving efficient and reliable operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key factors that should be considered when selecting a brake motor:
1. Load Characteristics: The characteristics of the load being driven by the brake motor are essential considerations. Factors such as load size, weight, and inertia influence the torque, power, and braking requirements of the motor. It is crucial to accurately assess the load characteristics to select a brake motor with the appropriate power rating, torque capacity, and braking capability to handle the specific load requirements effectively.
2. Stopping Requirements: The desired stopping performance of the brake motor is another critical factor to consider. Different applications may have specific stopping time, speed, or precision requirements. The brake motor should be selected based on its ability to meet these stopping requirements, such as adjustable braking torque, controlled response time, and stability during stopping. Understanding the desired stopping behavior is crucial for selecting a brake motor that can provide the necessary control and accuracy.
3. Environmental Conditions: The operating environment in which the brake motor will be installed plays a significant role in its selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, vibration, and corrosive substances can affect the performance and lifespan of the motor. It is essential to choose a brake motor that is designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of the application, ensuring reliable and durable operation over time.
4. Mounting and Space Constraints: The available space and mounting requirements should be considered when selecting a brake motor. The physical dimensions and mounting options of the motor should align with the space constraints and mounting configuration of the application. It is crucial to ensure that the brake motor can be properly installed and integrated into the existing machinery or system without compromising the performance or safety of the overall setup.
5. Power Supply: The availability and characteristics of the power supply should be taken into account. The voltage, frequency, and power quality of the electrical supply should match the specifications of the brake motor. It is important to consider factors such as single-phase or three-phase power supply, voltage fluctuations, and compatibility with other electrical components to ensure proper operation and avoid electrical issues or motor damage.
6. Brake Type and Design: Different brake types, such as electromagnetic brakes or spring-loaded brakes, offer specific advantages and considerations. The choice of brake type should align with the requirements of the application, taking into account factors such as braking torque, response time, and reliability. The design features of the brake, such as braking surface area, cooling methods, and wear indicators, should also be evaluated to ensure efficient and long-lasting braking performance.
7. Regulatory and Safety Standards: Compliance with applicable regulatory and safety standards is crucial when selecting a brake motor. Depending on the industry and application, specific standards and certifications may be required. It is essential to choose a brake motor that meets the necessary standards and safety requirements to ensure the protection of personnel, equipment, and compliance with legal obligations.
8. Cost and Lifecycle Considerations: Finally, the cost-effectiveness and lifecycle considerations should be evaluated. This includes factors such as initial investment, maintenance requirements, expected lifespan, and availability of spare parts. It is important to strike a balance between upfront costs and long-term reliability, selecting a brake motor that offers a favorable cost-to-performance ratio and aligns with the expected lifecycle and maintenance budget.
Considering these factors when selecting a brake motor helps ensure that the chosen motor is well-suited for the intended task, provides reliable and efficient operation, and meets the specific requirements of the application. Proper evaluation and assessment of these factors contribute to the overall success and performance of the brake motor in its designated task.
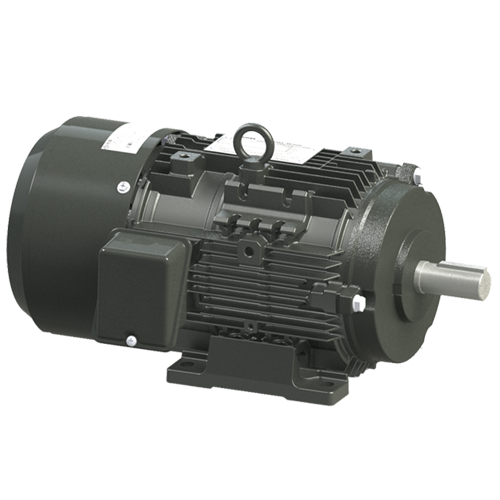

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-04-16